Understanding the Very Basics of Drum Theory: A Must for Every Drummer
- Marios Karavasilis

- Jan 27
- 3 min read
Updated: Feb 14
Why Basics of Drum Theory Matters
Drum theory often feels like a mysterious world reserved for advanced musicians, but the truth is, it’s the foundation that every drummer—from beginner to pro—should build upon. Imagine being able to read rhythms fluently, understand time signatures instinctively, and create patterns with purpose. That’s what drum theory offers.
In this post, we’ll explore the basics of drum theory that every drummer should know, focusing on practical knowledge you can apply directly to your playing. By the end, you’ll see how even a little theory can make a big difference in your drumming journey.
Table of Contents

The Staff: A Drummer’s Blueprint
The staff is at the heart of drum theory, the series of five horizontal lines where drum notation lives. But unlike other instruments, drummers don’t play pitched notes; we focus on rhythm and placement.

Here’s how it works:
Each line and space on the staff corresponds to a specific part of the drum kit:
Snare drum: 3rd space.
Bass drum: 1st space.
Hi-hat: Above the staff, often marked with an ‘x’.
The Percussion Clef: A unique symbol that tells us the notation is for unpitched instruments.
Understanding the staff helps you read grooves, fills, and rhythms that might otherwise seem intimidating. It’s like learning a new language—challenging at first, but immensely rewarding.
Time Signatures: The Framework for Rhythm
Time signatures tell drummers how music is organized:
Top number: How many beats are in each measure?
Bottom number: What kind of note (e.g., quarter note) gets one beat?

For example:
4/4 time: The most common signature in modern music. You count “1, 2, 3, 4” in each measure.
6/8 time: A flowing, triplet-based rhythm often used in ballads or folk music.
When you understand time signatures, you’re no longer guessing how many beats fit in a bar. You’re laying the groundwork for creating consistent grooves that lock in with the music.
Note Values: Understanding Duration
Every rhythm is built from note values, which indicate how long each note or rest lasts. Here’s a quick breakdown:
Whole note: 4 beats.
Half note: 2 beats.
Quarter note: 1 beat.
Eighth note: ½ beat.
Sixteenth note: ¼ beat.
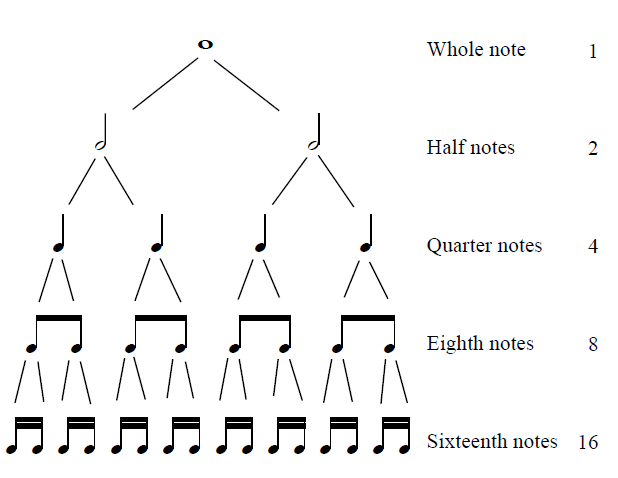
Knowing these durations allows you to interpret and execute rhythms accurately, whether it’s a steady rock groove or a complex fill. Counting out loud (e.g., “1 e & a 2 e & a”) is an excellent way to internalize note values.
How Drum Theory Fuels Creativity
Many drummers worry that learning theory will stifle creativity, but the opposite is true. Theory gives you tools to:
Build grooves with intention: Understanding subdivisions and syncopation helps you craft patterns that add character to a song.
Improvise effectively: Knowing note values and rests allows you to experiment with dynamics and phrasing.
Communicate with other musicians: Whether it’s following a chart or jamming with a band, theory ensures you’re speaking the same musical language.
Start Applying Theory Today
Here are a few actionable steps to bring drum theory into your practice:
Learn the Staff:
Memorize the placement of the snare, bass drum, and, hi-hat on the staff.
Practice Counting:
Use a metronome to practice quarter, eighth, and sixteenth notes. Focus on consistency.
Read Simple Charts:
Start with basic drum notation for familiar songs to build confidence.
Take the Next Step
Understanding the very basics of drum theory is just the beginning. For a deeper dive into topics like dynamics, syncopation, and advanced notation, download our free guide: “Music Theory for Drummers!” This comprehensive resource breaks down complex ideas into simple, actionable steps tailored for drummers.
Subscribe to the DrumOrama Newsletter today and gain instant access to this invaluable guide.
Whether you’re just starting or looking to refine your skills, this is your key to drumming with confidence and creativity.
Build Your Foundation
Drum theory isn’t just for academics—it’s a practical tool for transforming your playing. By understanding the staff, time signatures, and note values, you’ll not only improve your technical skills but also unlock new levels of musicality.
Take the first step by applying these concepts in your practice today. And don’t forget to download our free guide to continue your journey toward drumming mastery!






Comments